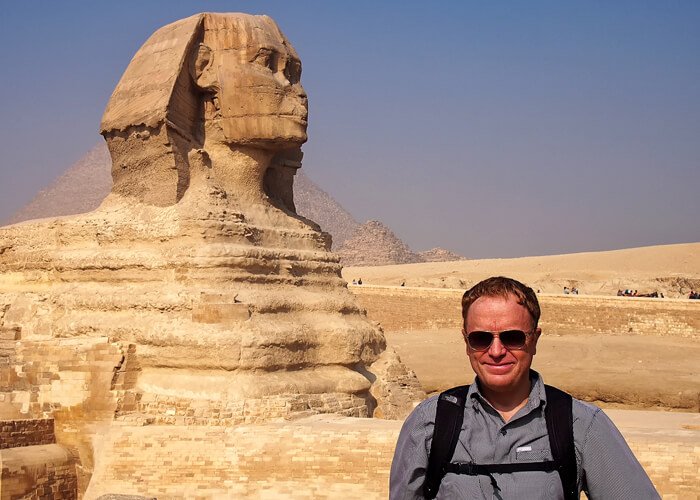
Great Sphinx of Giza
Perched on the Giza Plateau just beyond the shadow of the Great Pyramid, the Great Sphinx of Giza stands as an enduring symbol of ancient ingenuity, mystery, and grandeur. Carved from a single limestone ridge more than 4,500 years ago, this colossal limestone statue—featuring a lion’s body and a human head—draws millions of visitors each year eager to decipher its secrets. In 2025, the Great Sphinx remains one of the world’s most captivating monuments, blending myth and reality in a way few archaeological sites can match. Whether you’re a history buff, a photography enthusiast, or simply someone seeking an unforgettable travel experience, understanding the Sphinx’s story is the first step toward an enriching journey.
Key Takeaways
- Iconic Legacy: The Great Sphinx of Giza is one of the oldest and largest monumental sculptures in the world.
- Construction Timeline: Believed to have been carved around 2500 BCE during the reign of Pharaoh Khafre.
- Architectural Features: A massive statue—approximately 73 meters long and 20 meters high—meticulously hewn from natural bedrock.
- Symbolic Significance: Represents royal power, guardianship, and theological concepts of the sun god.
- Restoration Efforts: Ongoing preservation initiatives have taken place from the 19th century through to 2025.
- Visitor Experience in 2025: New protective barriers, improved viewing platforms, and guided tour options elevate the modern visit.
- Tour Planning Tips: Best times to visit, ticketing advice, and must-see nearby attractions.
- Travel Agency Services: Customized private and group tours from Cairo and Luxor, expert local guides, and VIP access packages.
A Monument Born of Kings and Myth
The Great Sphinx of Giza was carved directly into the Giza Plateau’s natural limestone outcrop, likely as a symbol of the pharaoh’s divine authority. Most scholars agree that its face bears the likeness of Pharaoh Khafre (c. 2558–2532 BCE), who ruled during Egypt’s Fourth Dynasty. Over millennia, shifting sands buried the body to its neck, preserving its contours but eroding finer details. Rediscovered in the early 19th century, the Sphinx has since endured repeated excavations and restorations, revealing layers of history concealed beneath centuries of sand.
While the exact motivations behind its construction remain debated, prevailing theories link the Sphinx’s role to solar worship—positioned to greet the sunrise and embody the rising sun’s life-giving power. In Egyptian cosmology, the lion’s body symbolized strength and kingship, while the human head conveyed intelligence and rulership. Together, these elements communicated a potent message: the pharaoh as both beast-mastery and divinely enlightened sovereign.
Architectural Marvels and Dimensions
Standing approximately 20 meters (66 feet) tall and 73 meters (240 feet) long, the Great Sphinx of Giza ranks among the world’s largest monolithic statues. Its scale is impressive even by modern standards—equivalent in length to three adult buses lined end to end. Carved from a single bedrock ridge, the statue’s body and base remain integral to the plateau, while the head and neck exhibit individually chiseled blocks added or repaired in antiquity.
- Head and Face: Though the nose and ceremonial beard are missing, the residual facial features demonstrate precise proportions and delicate carving techniques.
- Body and Paws: The broad, outstretched front paws and muscular hindquarters evoke a poised, watchful creature.
- Temple Complex: Directly in front of the Sphinx lies the Sphinx Temple, constructed of massive limestone blocks and thought to serve ritual functions related to solar worship.
Modern 3D laser scans and photogrammetry in 2025 have provided new insights into weathering patterns and structural stresses. These studies guide ongoing conservation efforts, ensuring that visitors can continue to appreciate the Sphinx’s grandeur without compromising its stability.
Myths, Legends, and Cultural Impact
Over centuries, the Great Sphinx of Giza has inspired myths both ancient and modern:
- The Dream Stele: Between the paws rests a granite stele erected by Pharaoh Thutmose IV (c. 1401–1391 BCE), recounting a vision in which the Sphinx promised to grant kingship to whoever cleared away the encroaching sands. This text underscores the Sphinx’s significance as an oracular and protective figure.
- Napoleon’s Nose Myth: A persistent but false tale attributes the Sphinx’s missing nose to cannon fire by Napoleon’s troops in 1798. In reality, sketches from the 18th century already depict the nose absent, suggesting earlier damage by local iconoclasts.
- Modern Pop Culture: From Hollywood films to video games, the Sphinx features prominently, often shrouded in supernatural lore. While these portrayals are dramatic, they rarely reflect the archaeological record.
Despite fanciful stories, the Sphinx’s true allure lies in its tangible connection to one of history’s most advanced civilizations. By grounding our understanding in evidence and scholarly research, travelers gain a deeper appreciation for the monument’s authentic significance.
Restoration and Preservation Through the Ages
Preserving a 4,500-year-old limestone statue in a harsh desert environment poses ongoing challenges. Restoration campaigns span three eras:
- 19th Century: Early excavations led by European explorers involved both beneficial clearing of sand and damaging removal of blocks, sometimes using primitive tools that harmed the underlying stone.
- 20th Century: Egyptian antiquities authorities implemented systematic conservation, including reinforcing crumbling stone with cement and adding protective barriers to limit visitor contact.
- 21st Century to 2025: Advances in materials science have introduced reversible consolidants and micro-crystalline wax treatments that stabilize flaking surfaces without altering the stone’s appearance. Digital monitoring sensors track humidity, temperature, and micro-vibrations to alert conservators of emerging issues.
Today, strict visitor guidelines—such as no climbing and designated photography zones—help minimize human impact. Combined with controlled windbreaks and strategic drainage systems, these measures ensure the Great Sphinx remains structurally sound and visually stunning for generations to come.
Planning Your Visit in 2025
Best Time to Visit
- Early Morning: Beat the crowds and photograph the Sphinx in softer light, around 6:00–8:00 AM.
- Late Afternoon: Enjoy cooler temperatures and golden-hour hues from 4:00–6:00 PM.
- Avoid Midday: High sun angle and peak crowds from 10:00 AM–2:00 PM can diminish the experience.
Ticketing Tips
- Combined Pass: Purchase a Giza Plateau ticket that covers the Sphinx, Great Pyramid interior, and Solar Boat Museum.
- VIP Early Access: Book at least two weeks in advance to secure a small-group entry before the site officially opens.
- Student and Senior Discounts: Available on presentation of valid ID at the ticket office.
Photography Guidelines
- Tripod Use: Allowed only during designated hours (typically pre-opening).
- Drones: Strictly prohibited without express permit from the Supreme Council of Antiquities.
- Flash Photography: Permitted—but use sparingly to protect the limestone from light-related degradation.
Nearby Attractions
- Great Pyramid of Khufu: A five-minute walk west of the Sphinx.
- Khafre Valley Temple: Adjoins the Sphinx Temple; combines seamlessly into your Sphinx tour.
- Solar Boat Museum: Houses the reconstructed “solar barque” of Khufu, a short drive north of the plateau.
Why Book Through Our Agency?
As specialists in tailored Egypt travel experiences, we combine local expertise with decades of industry knowledge:
- Customized Itineraries: Choose from half-day Sphinx-focused excursions or multi-day cultural immersions covering Luxor, Aswan, and beyond.
- Expert Egyptologists: All tours are led by licensed guides fluent in English, French, Spanish, and Mandarin.
- Seamless Logistics: Private transfers from Cairo International Airport, luxury accommodations, and skip-the-line entry where available.
- Sustainable Practices: We partner with eco-friendly hotels and support community-based initiatives in Giza.
In 2025, our agency introduces private nighttime Sphinx viewings under moonlight (subject to lunar calendar), complete with commentary on the site’s astronomy alignments and mythology—a once-in-a-lifetime experience for curious travelers.
Insider Tips for a Memorable Experience
- Stay Hydrated: Even in cooler months, the Giza Plateau can be arid. Carry at least one liter of water per person.
- Dress Comfortably: Lightweight, breathable fabrics and sun protection (hat, sunglasses, sunscreen) are essential.
- Respect Local Customs: Modest attire is appreciated around religious sites.
- Engage Your Guide: Ask about the Sphinx’s rumored underground chambers—modern archaeology continues to probe what lies beneath.
- Combine Sightseeing: Pair your Sphinx visit with a sound-and-light show at the Pyramids in the evening for a fuller cultural immersion.
Beyond the Plateau: Exploring Giza and Cairo
While the Great Sphinx of Giza commands center stage, the broader Giza area offers rich contrasts:
- Giza Zoo: A century-old botanical and zoological garden, ideal for families.
- The Egyptian Museum (Cairo): Houses the full Tutankhamun collection and thousands of artifacts tracing 5,000 years of Egyptian history.
- Coptic Cairo: A short drive provides a glimpse into Egypt’s Christian heritage with ancient churches and the Hanging Church.
- Khan el-Khalili Bazaar: Maḥkamet for hand-crafted souvenirs, spices, and traditional coffeehouses in Old Cairo.
A well-paced itinerary allows travelers to balance the Sphinx’s ancient majesty with Cairo’s vibrant urban tapestry.
Preparing for Your Trip: Practical Considerations
- Visa Requirements: Most nationalities can obtain an e‑visa before arrival; check validity and processing times in advance.
- Health & Safety: Routine vaccinations are recommended; bring any personal medications and a basic first-aid kit.
- Currency: Egyptian pound (EGP). ATMs are widespread, but carry small bills for tips (“baksheesh”) at archaeological sites.
- Connectivity: Free Wi-Fi hotspots exist in many hotels; consider purchasing a local SIM card for reliable mobile data.
- Travel Insurance: Essential, covering trip cancellation, medical evacuation, and lost belongings.
By sorting these details early, you ensure a stress‑free journey focused entirely on the marvels of 2025’s Great Sphinx of Giza experience.
Conclusion
The Great Sphinx of Giza transcends mere stone and sand—embodying centuries of royal ambition, religious devotion, and human curiosity. In 2025, this monumental guardian continues to captivate travelers, scholars, and storytellers around the globe. Whether you stand before its mighty paws at dawn’s first light or contemplate its enigmatic gaze beneath a full moon, the Sphinx invites you to connect with a civilization whose legacy still shapes our world today.
Plan your visit with confidence: let our seasoned guides and bespoke itineraries transform your dream of Egypt into an effortless reality. Embark on a journey where past and present converge, and discover why the Great Sphinx of Giza remains, above all else, the enduring heart of Egypt’s timeless allure.



Comments are closed